How to Optimize Images for SEO

Short Answer: To optimize images for SEO, choose the right file format, compress for speed, write descriptive filenames and alt text, and add structured data so search engines and AI systems can understand what your visuals represent. The goal isn’t just to rank in Google Images; it’s to make every image on your site discoverable, descriptive, and AI-ready.
Why Image Optimization Matters More Than Ever
Images used to be aesthetic flourishes. Today, they’re search signals. Google and AI systems now analyze image context, captions, and even textures to determine relevance. A well-optimized image can improve your visibility in image search, boost engagement, and even help your content appear in AI-driven summaries and visual previews.
According to Google’s official image documentation, images are ranked based on both visual relevance and page context, meaning the quality of your surrounding content matters just as much as the pixels themselves.
Optimizing your images doesn’t just make them easier to find. It helps Google understand them, which is a crucial distinction in the AI era of multimodal search.
1. Choose the Right Image Format
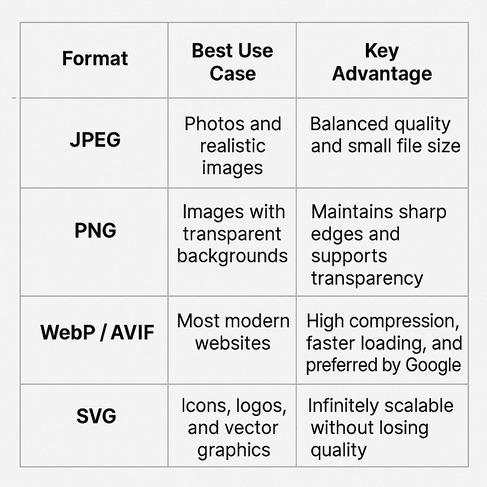
Every image format serves a different purpose:
-
JPEG: Best for photos and realism
-
PNG: Ideal for transparent backgrounds
-
WebP or AVIF: High compression, faster loading, and preferred by Google
-
SVG: Best for icons and vector graphics
Once you’ve picked the right format, size it correctly before uploading. Large banner images, in particular, can slow your site down if they’re not resized for web display. My favorite free tool for this is ImageResizer.com. I use it to resize banner images for almost every blog and landing page I publish. It’s quick, simple, and helps me keep image dimensions consistent across my portfolio.
For SEO purposes, I aim to keep each image file around 100 KB or less whenever possible. It’s a small adjustment that significantly improves load speed and Core Web Vitals, especially on mobile.
Where possible, serve responsive versions using the srcset attributes so browsers can load the right size for each device.
2. Rename Your Files Intentionally

Before uploading, rename your files descriptively. Instead of IMG_0024.jpg, use something like honda-passport-towing-capacity-chart.jpg.
The filename helps search engines interpret what your image represents. It also keeps your site organized for future edits, audits, or re-uploads.
If you’re using multiple images on one topic, include descriptive modifiers like “front,” “dashboard,” or “dimensions” to clarify each image’s focus.
3. Write Descriptive, Human-Readable Alt Text
Alt text is your image’s translator. It tells search engines and visually impaired users what’s in the picture.
Effective alt text should:
-
Describe the content accurately
-
Include a natural keyword if relevant
-
Avoid repetition or keyword stuffing
Example:
❌ Bad: “Car car car vehicle Honda best SUV.”
✅ Good: “2026 Honda Passport towing an RV trailer through the mountains.”
If you’re having trouble describing all the elements of an image, try uploading it to ChatGPT and asking it to write alt text for you. You can then edit the description to make sure it matches your tone and SEO intent. It’s an easy way to generate accurate, descriptive alt text without missing visual details.
Alt text also helps AI systems interpret your visuals contextually. In Google’s newer “AI Overview” environment, that text often contributes to how the system summarizes your content visually, making it doubly valuable.
4. Add Structured Data for Images
Structured data tells search engines what kind of image they’re looking at, such as a product, recipe, article, or review.
Use the ImageObject schema to specify:
-
Image URL
-
Caption or description
-
License information
-
Associated article or product
If you’re running an ecommerce or blog site, link your ImageObject schema to Product or Article schema to reinforce topical connections.
This simple markup can help your image appear with badges, rich results, or AI-driven previews.
5. Optimize the Page Around the Image
Your image doesn’t rank alone; the page it lives on matters.
Include relevant keywords in:
-
Page title and meta description
-
H2 or H3 headings near the image
-
Caption or summary text
Surround the image with descriptive copy. Google’s visual crawlers assess the relationship between your text and visuals to decide how and where your image should appear.
Tip: Keep the image near its most relevant paragraph, not buried at the bottom of a long page.
6. Balance Quality and Speed
High-resolution images are eye-catching but can sabotage load times.
-
Compress aggressively but test for clarity
-
Use lazy loading so images appear only as users scroll
-
Host images on a CDN for faster global delivery
-
Run PageSpeed Insights or Lighthouse to measure visual load times
Remember, users abandon pages that load in more than three seconds, and Google notices. Fast-loading visuals make your page more indexable and rank-friendly.
7. Prepare for AI-Driven Visual Search
AI doesn’t just see your images; it interprets them. That’s why your metadata, file names, and alt text need to sound natural and contextual, not robotic.
In What Google’s New AI Mode Means for SEO Content Writers, I explain that image optimization is now part of content clarity because AI systems weigh visuals as evidence of your claims.
If your blog discusses “eco-friendly bathroom accessories,” showing a real product photo with descriptive alt text like “water-saving bamboo bathroom set” reinforces authenticity and helps AI confirm factual alignment.
Authentic visuals, not generic stock photos, will become the new trust signals.
8. Target Thumbnail Visibility in AI Overviews
When Google’s AI Overviews display thumbnail images beside citations, those visuals attract immediate clicks. Optimizing for this feature can significantly increase visibility, especially for brands competing in AI-driven SERPs.
According to AI Overview Image Thumbnails: How to Take Advantage, your best chances of earning a thumbnail include:
-
Using high-contrast, centered images with minimal text overlays
-
Implementing Open Graph (
og:image) and Twitter Card markup -
Ensuring the image appears early in your article or metadata
These small adjustments help your images qualify for thumbnail display, where attention and clicks cluster first.
9. Track and Iterate
Image SEO isn’t a one-time fix. Use Google Search Console to monitor which pages generate image clicks.
Metrics to track:
-
Impressions in Google Images
-
Click-through rates from image results
-
Performance of AI-featured thumbnails
-
Changes in page speed after optimization
Iterate gradually by starting with high-traffic pages or visual content hubs, then expanding site-wide.
10. Common Mistakes to Avoid
-
Using filenames like “image1.png” or “photo.jpg”
-
Leaving alt text blank or overstuffed
-
Uploading 3 MB+ images without compression
-
Using stock photos unrelated to the content
-
Ignoring structured-data validation errors
Even one of these can derail otherwise strong SEO performance.
FAQ: Image SEO Basics
1. Do image file names really affect SEO?
Yes. Google reads filenames to understand what the image depicts. A descriptive file name like honda-passport-towing-chart.jpg gives stronger context than IMG0024.jpg.
2. How often should I compress or update my images?
Check your Core Web Vitals at least quarterly. Recompress older images or switch them to WebP if your pages are loading slowly.
3. Can alt text include keywords?
Yes, but naturally. Write for clarity first, then weave in one relevant keyword if it fits the description.
4. Should I use the same image across multiple pages?
If it’s highly relevant, yes. Just make sure the surrounding text changes so each page provides unique context.
5. Do AI Overviews choose images automatically?
They do. That’s why metadata, Open Graph tags, and early image placement matter; they help AI decide which visuals to display in summaries.
Conclusion: Your Images Are Content, Too
Optimizing your visuals isn’t about tricking algorithms; it’s about creating images that make sense to both humans and AI.
Every filename, caption, and schema tag adds semantic value. Each optimized image becomes another opportunity to be discovered across Google Images, AI Overviews, and voice-based visual results.
Audit your top pages today, compress images, refine alt text, add schema, and test your speed. Your visuals can become your next major SEO advantage.
Need help optimizing your images for AI search visibility? Reach out to get personalized SEO content and image optimization support designed for the AI era.

0 Comments Add a Comment?